Order
This sub process consists of the following activities:
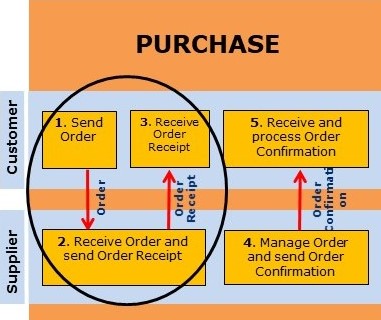
- Send order
- Receive orders and return order receipt
- Receive order receipt
Areas affected by, and subject to guidelines from STAND are:
- How EDI is used in the retail trade in general and in the ordering process in particular
- Requirements for EDI messages
- EDI exchange agreement
- Generic description of the ordering process
- Bilateral agreements on the assessment of shelf life on products covered by this
Use of EDI in the retail trade
EDI – Electronic Data Interchange – is used in the retail industry to exchange commercial documents like Order, Order Receipt, Order Confirmation, Despatch Advice, Invoice and Invoice Receipt.
EDI can be performed in various ways, from fully automated processes both at customer and supplier, to web solutions where information is registered manually.
EDI is used for all distribution types.
Overview of EDI messages and in which processes they are used
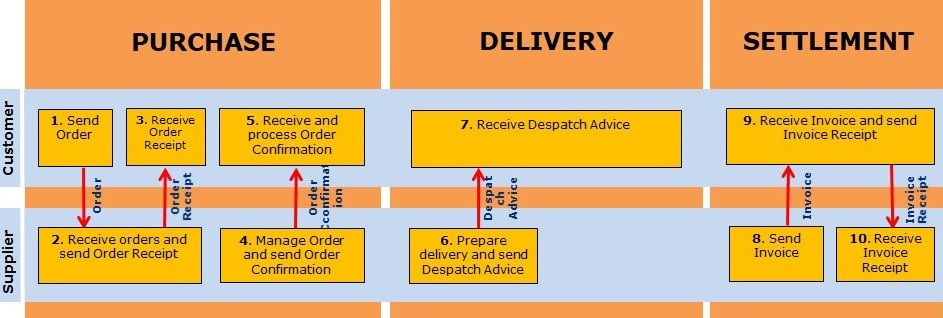
Which EDI messages to use will vary with the distribution type.
An overview of this, along with deadlines for when the messages are to be sent, are described in EDI message, type of distribution and deadlines.
Before using EDI, it is necessary to clarify which messages to be used, message formats, exchange methods, electronic message addresses, etc. This documented the EDI Exchange agreement.
This document also specifies other bilateral issues related to the exchange of EDI messages.
To ensure that both parties and all business functions are familiar with all bilateral agreements, it is crucial that the EDI Exchange Agreement is used actively.
How to get started with EDI is described in Implement EDI in the retail trade.
In order to start using EDI, trading documents must be translated into an EDI format.
The following formats are available:
- Message description EANCOM for order, order receipt, order confirmation, Despatch Advice, invoice, invoice receipt
- Message description XML for order, order receipt, order confirmation, Despatch Advice, invoice, invoice receipt
Revisions of the EDI formats, is documented in Change log current version vs. past versions
Order
Send order
An order is sent in the form of an EDI order, and specifies products / services ordered under the terms agreed between seller and buyer.
The order shall fulfil bilateral agreements specified in the EDI exchange agreement.
The order includes buyer and seller, product, quantity, desired delivery date and place of delivery.
The order must be sent in accordance with the agreed order stop time.
Possible corrections that can be made on an order after it has been sent:
- Cancellation of the order can be done in the following alternative ways:
- It is agreed on the telephone that the supplier must send an EDI order confirmation, with 0 in the amount on all product lines
- It is agreed on the telephone that the order is manually deleted in the system of both parties
- Additional Orders for delivery at the same time as the main order must be made within the agreed order stop time for the main delivery. This is done by placing an ordinary EDI order on the products and quantities to be ordered as well.
- Amendments on a dispatched order can be made in the following alternative ways:
- It is agreed that an EDI order confirmation will be sent with 0 on the item lines to be changed, upon which a new EDI order will be sent on the item lines that should be changed
- It is agreed on the phone that the original order is deleted, and that a new EDI order will be sent
- It is agreed on the telephone that an EDI order confirmation will be sent with 0 on all product lines, and there will then be sent a new EDI order
Special relationships related to order
The order number should be unique to each order sent from a buyer.
The supplier must reject an order where the order number is received and processed earlier.
For certain products, there is a bilateral agreement on how to split shelf life between the parties. Look to The establishment of bilateral agreements for the assessment of shelf life.
For EXW delivery terms, the rules dictate one order should only include one delivery from one pick-up point to one place of delivery and one desired delivery date.
For delivery terms where the supplier is responsible for transportation, the same applies, except that the order may contain deliveries from multiple locations.
Receipt of orders and return of order receipt
The supplier, if agreed upon in the EDI Exchange Agreement, shall return an EDI order receipt immediately after the order is received.
Order receipt has the function of confirming to the customer that the supplier has received the order. Order receipt contains no information on whether the customer receives the ordered products.
Receive order receipt
Upon reception of order receipt, it provides the customer with an assurance that the order was received by the supplier.
How order receipt is further used by the customer in internal systems is not covered by the guideline.
