Implementation of EDI in the retail trade
Introduction to implementation of EDI in the retail trade where STAND’s guidelines are to be used.
Before an exchange of EDI can take place, an EDI exchange agreement must be established.
This specifies all relevant information, such as:
- Which parties are covered by the EDI agreement
- Contacts for different functions at customer and supplier
- Addresses to be used when exchanging EDI messages
- Which EDI messages to be exchanged
- What format and version of EDI messages that are used
- The way in which EDI messages are exchanged
In addition, the EDI exchange agreement shall state all bilateral agreements relating to EDI Interaction.
Bilateral agreements shall be established in all areas where deviations from other guidelines in STAND, which involve EDI, arise. This may be:
- Processes
- Deadlines
- Content in EDI messages
Some important clarifications
Valid formats of messages
STAND supports two main formats;
- EANCOM, based on UN EDIFACT-format
- XML, self-developed and customized EANCOM format, except for customized invoice e2b Invoice
In addition, some customers accept other formats, but description of these is not part of the STAND guidelines.
The most used of other formats are
- EHF, developed by DIFI
- e2b Invoice
Both are XML-based
Exchange methods
There are different ways to exchange EDI messages. This is not regulated in STAND, but is agreed between the parties. The most relevant methods of exchange are:
- Exchange messages via a mailbox feature. This involves a third party who communicates inbound and outbound messages between the customer and the supplier’s mailbox
- Customer and supplier agree that messages are sent directly to each other’s server without the use of a third-party actor
- Supplier sends and receives messages via a web-portal
Introduction to technical documentation EDI
In the following, conditions are described which, regardless of the format in which EDI messages are exchanged, are common and must be assessed/taken into account when implementing EDI.
The target group for the documentation is technical personnel who will implement EDI in the IT solutions at the customer or supplier.
However, it is highly recommended that the documentation is be reviewed together with the customer / supplier’s business department, as describe in detail what needs to be considered for expected interaction to take place.
Technical documentation describes message flow and interaction related thereto for all processes where EDI is used, and deals with the messages:
- Order
- Order Receipt
- Order Confirmation
- Despatch Advice
- Invoice
- Invoice Receipt
As messages and interaction may vary for each type of distribution, the documentation is divided into three parts, one for each of the distribution forms:
- Delivery via distributor
- Delivery directly to retailer
- Crossdock
The guidelines emphasize that the exchange of messages and interaction must take place according to simple and clear principles that also make control and follow-up as simple as possible.
Despite this, bilateral agreements must be concluded in several areas. These are described for each form of distribution and process in subsequent documentation.
Bilateral agreements must be documented in the EDI exchange agreement.
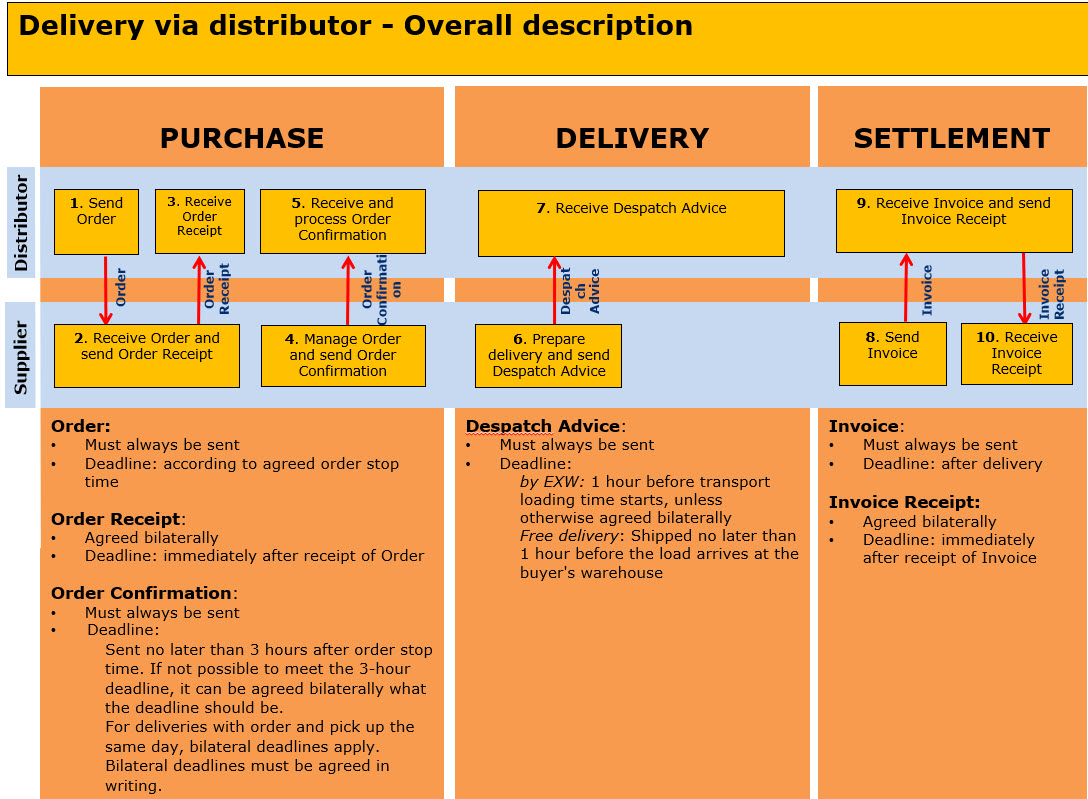
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- If Order Receipt shall be sent
- Deadline for Order Confirmation
- If Deviation from deadline on Despatch Advice at EXW
- If Invoice Receipt shall be sent
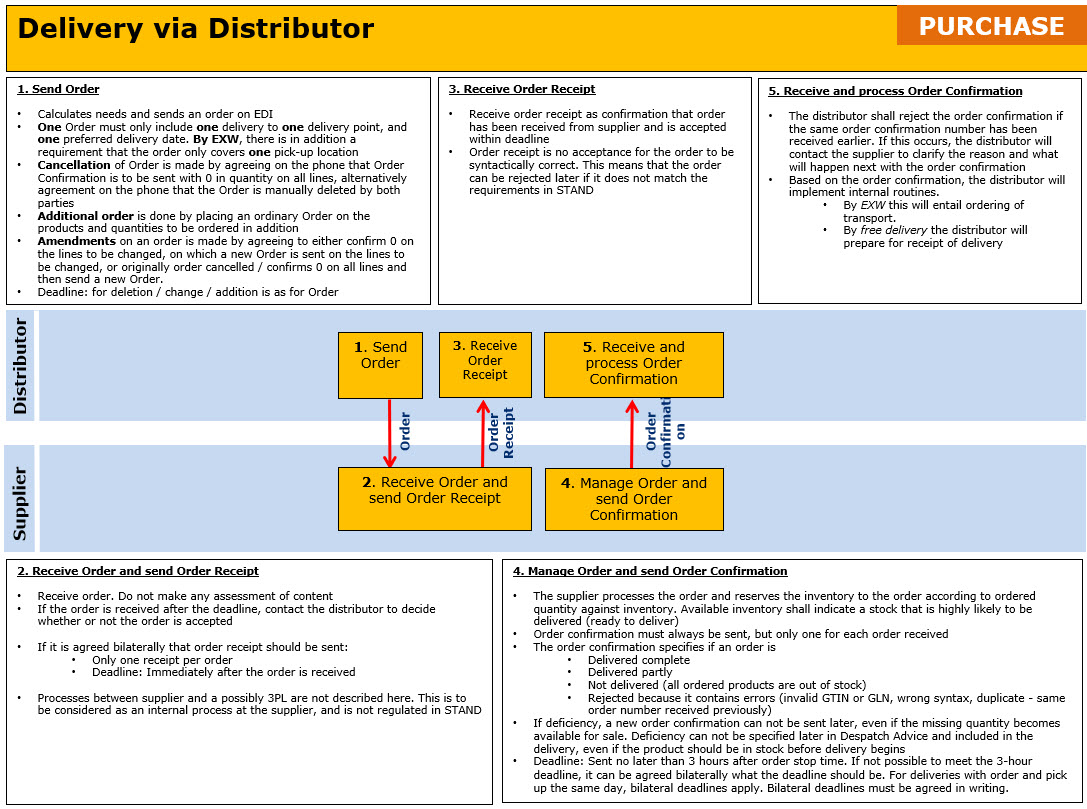
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- Order
- If order type Forecast shall be used and how this process is to be carried out
- If order type Industrial Sales / Representative orders shall be used and how this process will be carried out if this deviate from ordinary process
- Requested delivery / pick-up date. If the following codes are to be used:
- Latest delivery time
- Earliest delivery time
- Requested delivery for a week beginning with …
- If free text information should be sent, and which associated codes to be used
- Order confirmation
- If Quantity delivered will be sent. Not recommended to use because deviations from ordered quantity are added in a separate field defined for this
- If Availability date of product for temporary sold out, is to be sent
- If free text information should be sent, and which associated codes to be used
- Deadline for when Order Confirmation must be sent
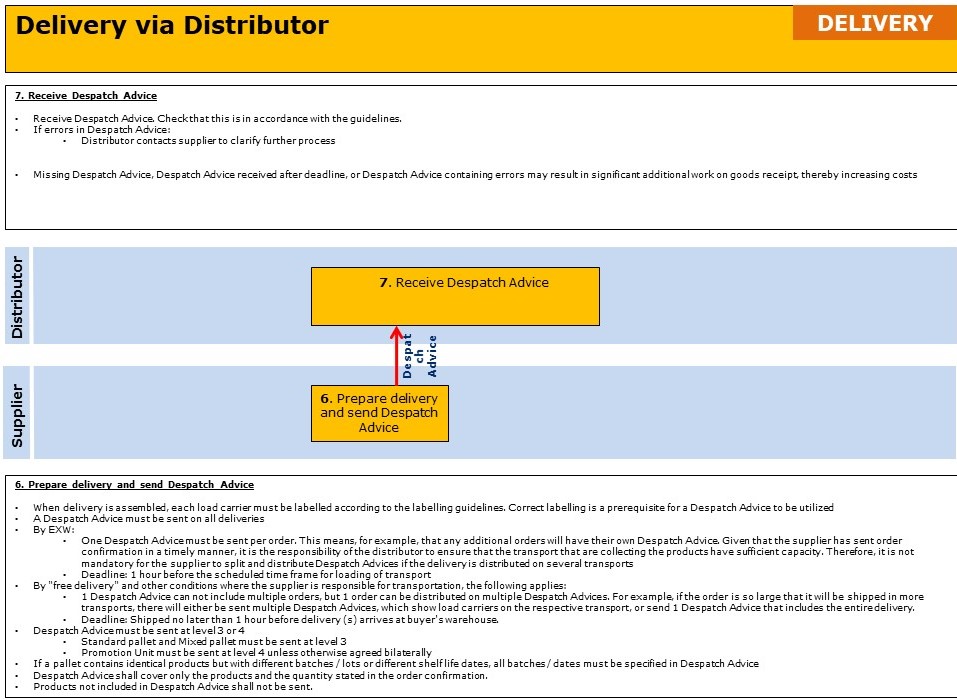
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- Despatch Advice
- If number of load carriers included in the pallet exchange scheme will be sent
- If number of pallet places the shipment requires in transport will be sent
- If Promotional Unit will be sent at level 3 in the Despatch Advice
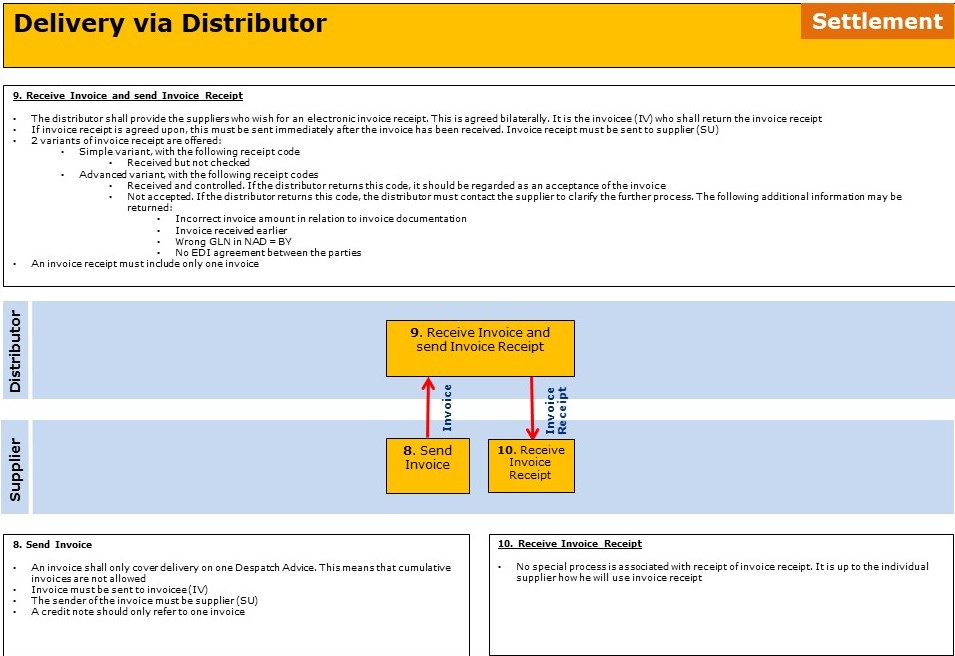
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- If simple or advanced version of Invoice Receipt must be sent
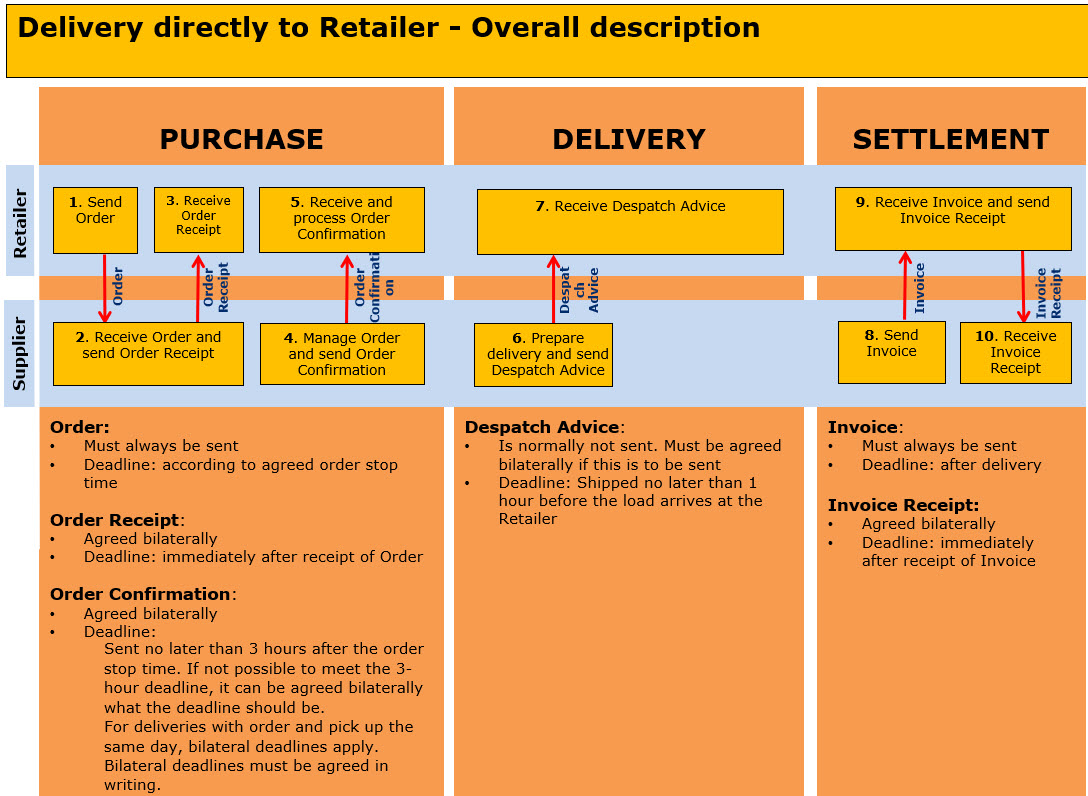
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- If Order Receipt shall be sent
- If Order Confirmation shall be sent
- Deadline for Order Confirmation
- If Despatch Advice shall be sent
- If Invoice Receipt shall be sent
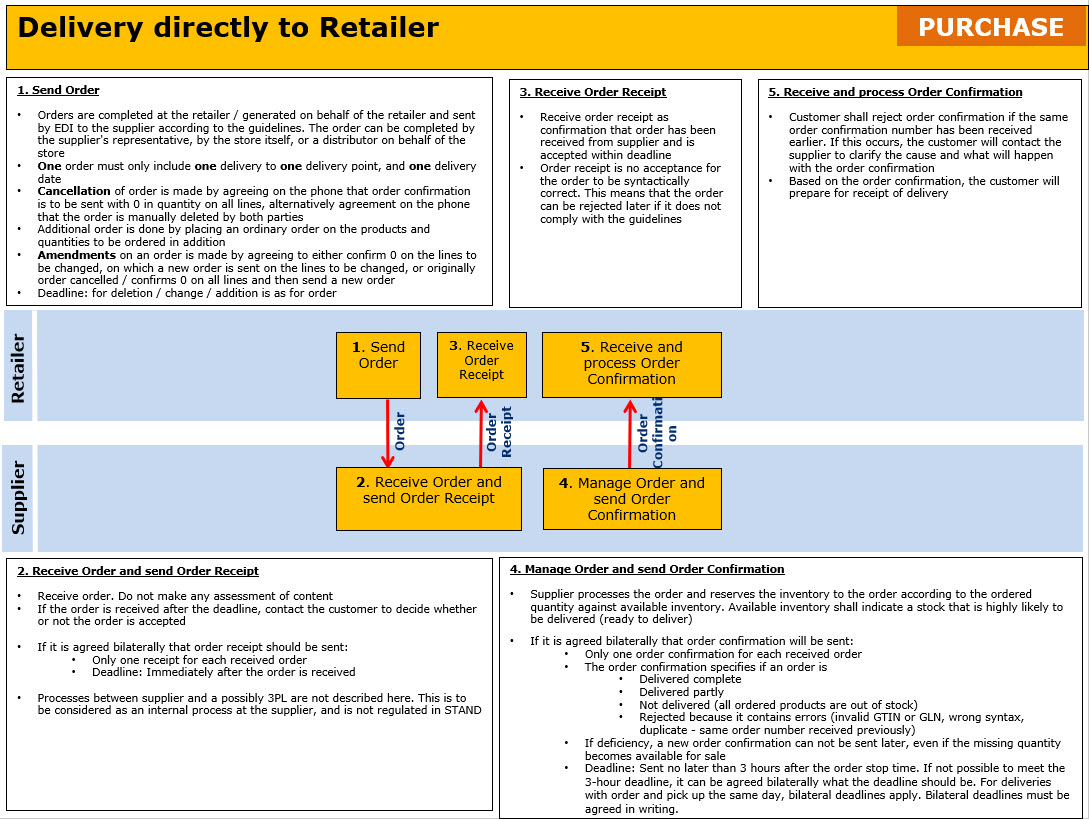
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- Order
- If order type Industrial Sales / Representative orders shall be used and how this process will be carried out if this deviate from ordinary process
- Requested delivery / pick-up date. If the following codes are to be used:
- Latest delivery time
- Earliest delivery time
- Requested delivery for a week beginning with …
- If free text information should be sent, and which associated codes to be used
- Order Confirmation
- If Quantity delivered will be sent. Not recommended to use because deviations from ordered quantity are added in a separate field defined for this
- If Availability date of product for temporary sold out, is to be sent
- If free text information should be sent, and which associated codes to be used
- Deadline for when Order Confirmation must be sent
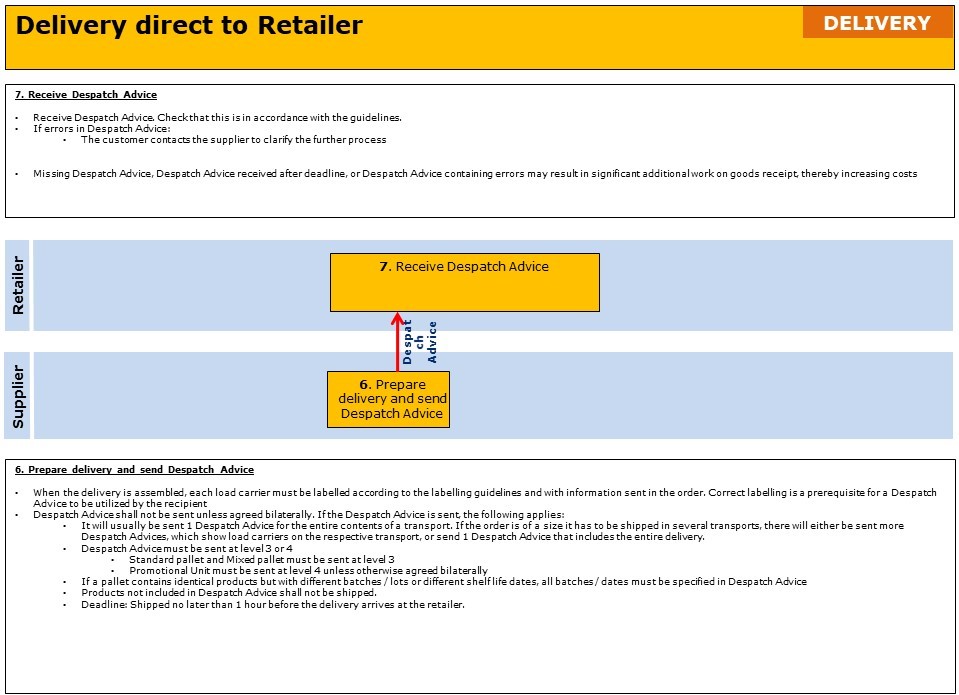
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- Despatch Advice
- If number of load carriers included in the pallet exchange scheme will be sent
- If number of pallet places the shipment requires in transport will be sent
- If Promotional Unit will be sent at level 3 in the Despatch Advice
- If Quantity (ordered quantity) will be sent (can only be used if Order Confirmation is not used)
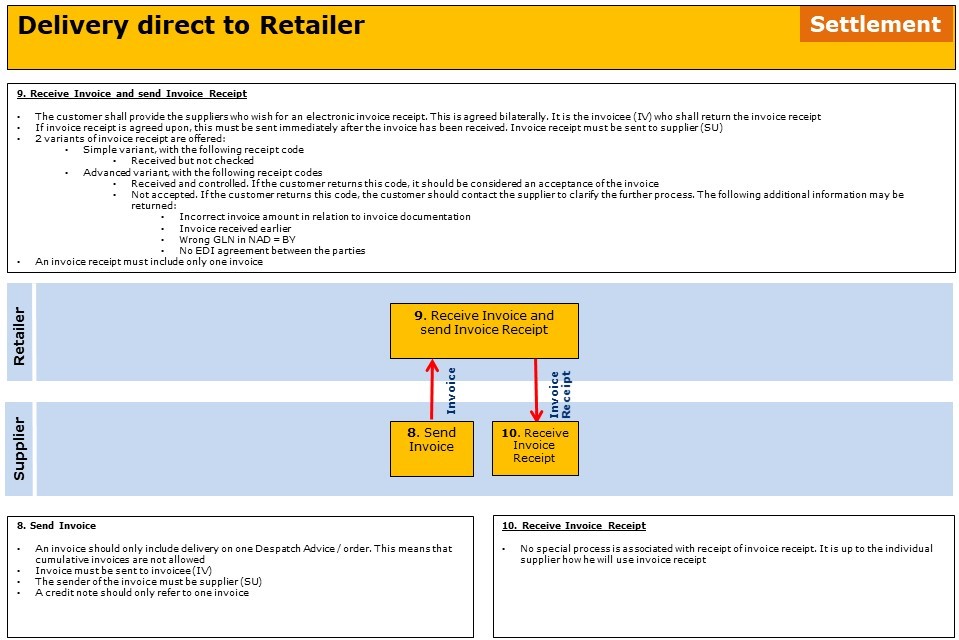
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- If simple or advanced version of Invoice Receipt must be sent
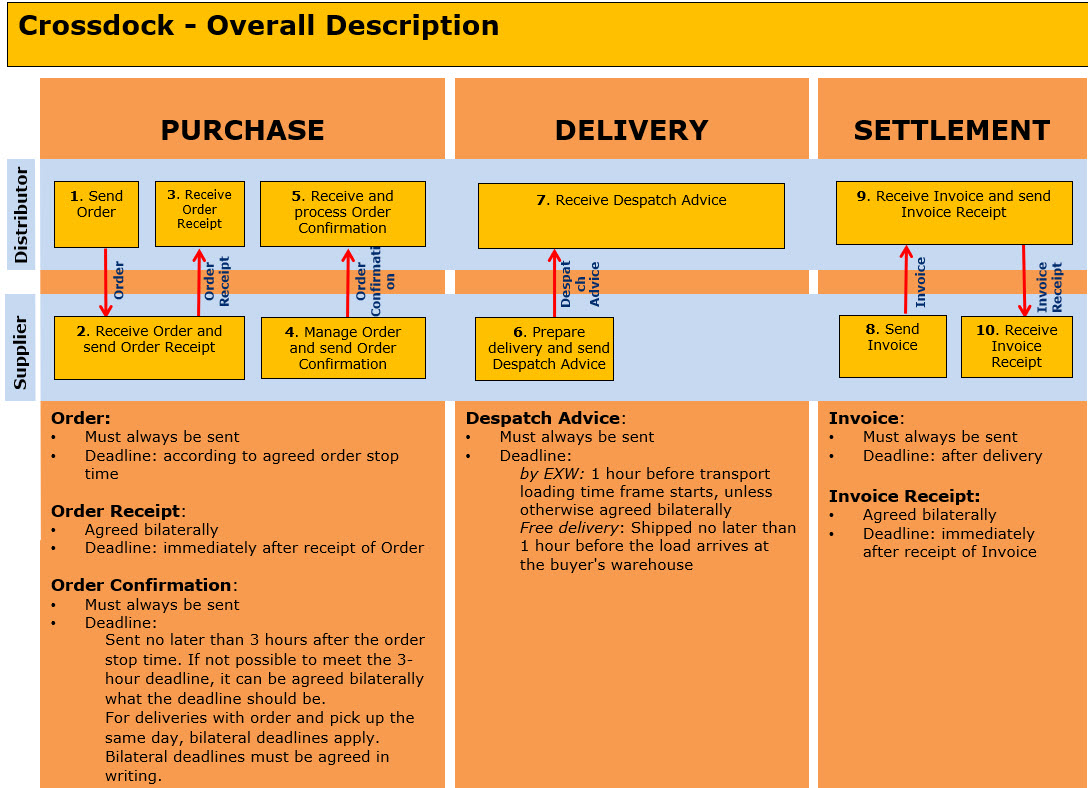
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- If Order Receipt shall be sent
- Deadline for Order Confirmation
- If Deviation from deadline on Despatch Advice at EXW
- If Invoice Receipt shall be sent
Special conditions at Crossdock
Replacement product (alternative product)
Use of replacement products must be agreed bilaterally. Replacement products can be used in connection with customer packed deliveries.
The principle is that original product ordered is replaced by alternate product from supplier. The supplier and the customer have agreed in advance which products are to be replaced. Order confirmation to describe the deviation between which product is ordered and which is delivered will not be used in this case.
It may occur that one product may be replaced with several replacement products.
Additional product lines
Use of additional products must be agreed bilaterally. Additional product lines can be used for customer packed deliveries.
The principle is that additional product lines are used if the products is not ordered in the original order but is ordered in retrospect (for example, by phone). The supplier and the customer have agreed in advance which products are to be replaced. Order Confirmation is not used in this case.
Customer packed deliveries from supplier
Identification of end customer / end receiver
In case of customer packed deliveries from the supplier, the main rule is that the end receiver is identified with GLN in the order notice. In special situations where the supplier has no access to GLN, the customer may send with the end receiver’s name and address information.
Handling Instructions
In case of customer packed deliveries from the supplier, the customers need to be informed about detailed transport information / handling instructions for Crossdocking on transit storage. This type of information is exchanged in the order notice.
Handling instructions sent from customer to supplier are specified as a structured free text field.
Indication of SSCC
Each unit of customer packed deliveries must be labelled with SSCC. Information about the individual devices and the connection to the SSCC is sent in the Despatch Advice.
Parties
At Crossdock, the buyer or product recipient shall identify the Crossdocking terminal. The end receiver shall then identify the recipient, which may be a warehouse or a store.
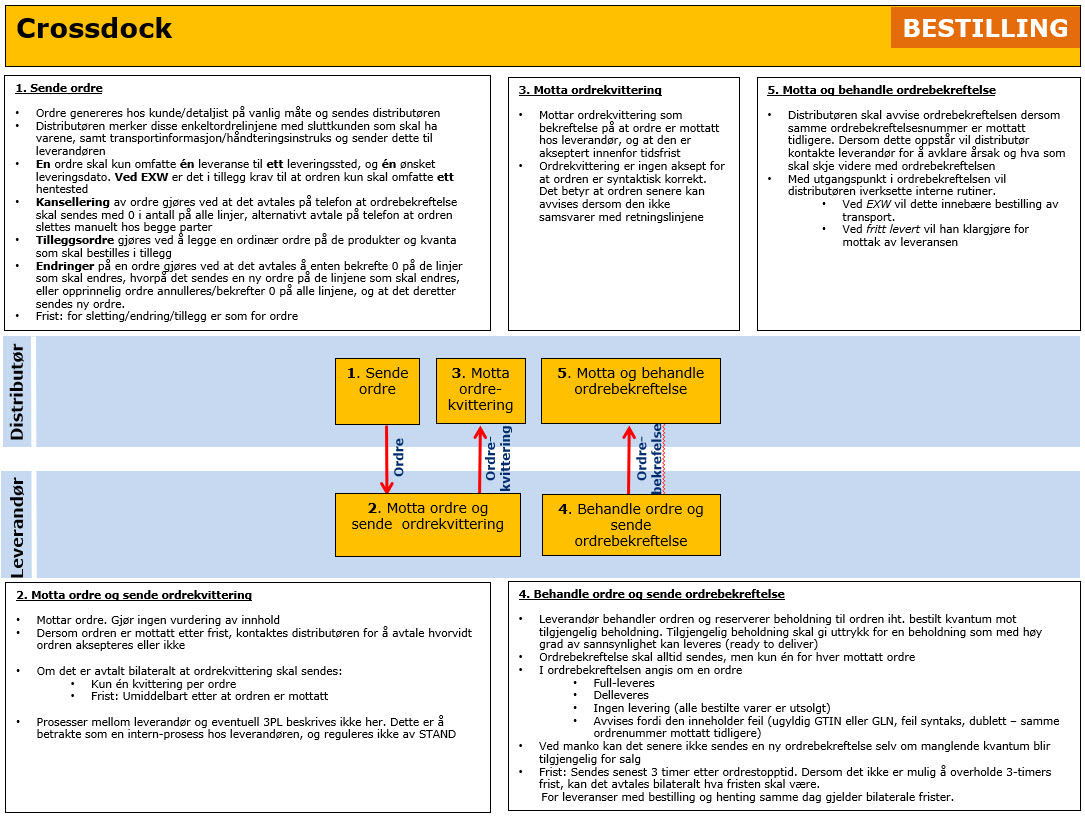
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- Order
- Requested delivery- / pick-up date. If the following codes are to be used:
- Latest delivery time
- Earliest delivery time
- Requested delivery for a week beginning with …
- If free text information should be sent, and which associated codes to be used
- Requested delivery- / pick-up date. If the following codes are to be used:
- Order Confirmation
- If Quantity delivered will be sent. Not recommended to use because deviations from ordered quantity are added in a separate field defined for this
- If Availability date of product for temporary sold out, is to be sent
- If free text information should be sent, and which associated codes to be used
- Deadline for when Order Confirmation must be sent
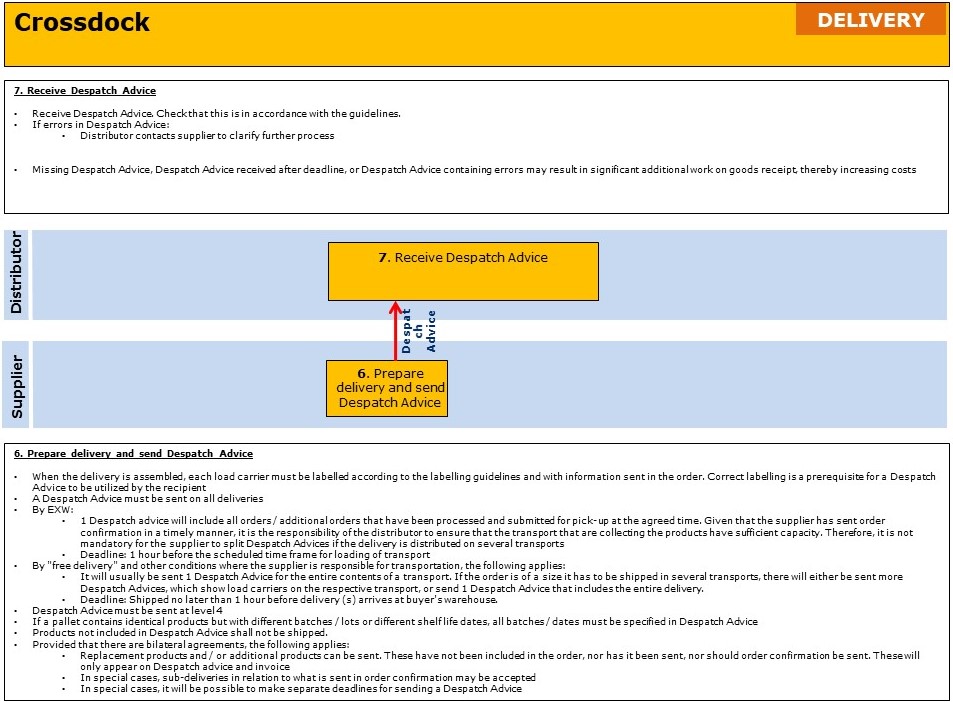
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- Despatch Advice
- If number of load carriers included in the pallet exchange scheme will be sent
- If number of pallet places the shipment requires in transport will be sent
- If Promotional Unit will be sent at level 3 in the Despatch Advice
- If Replacement product can be delivered
- If it is allowed to add products not ordered in the delivery / Despatch Advice
- If Ultimate Customer of delivery can be sent at line level
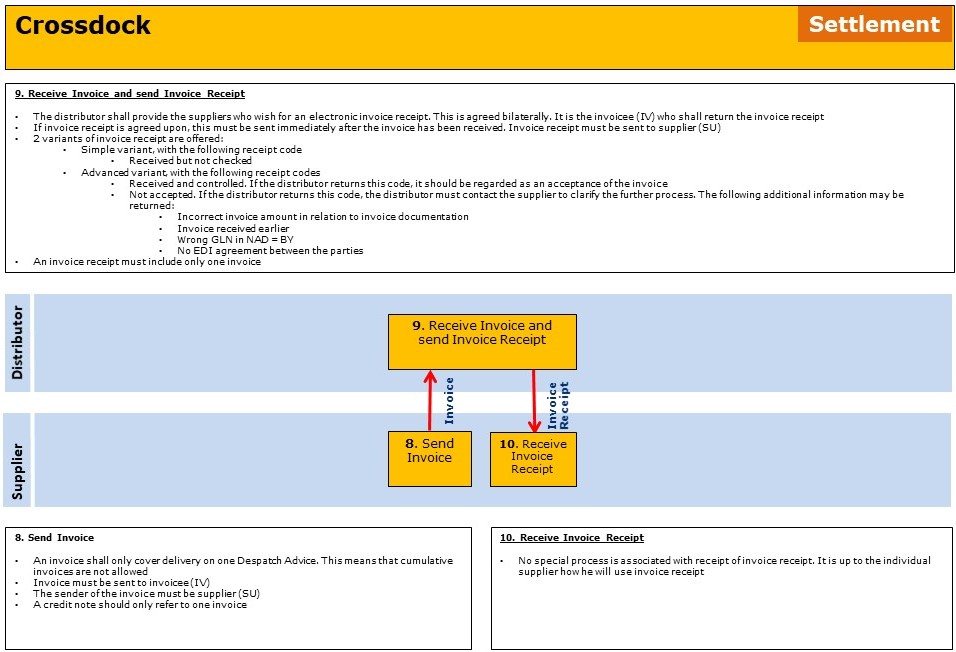
Areas where bilateral agreements can be established is:
- If simple or advanced version of Invoice Receipt must be sent
